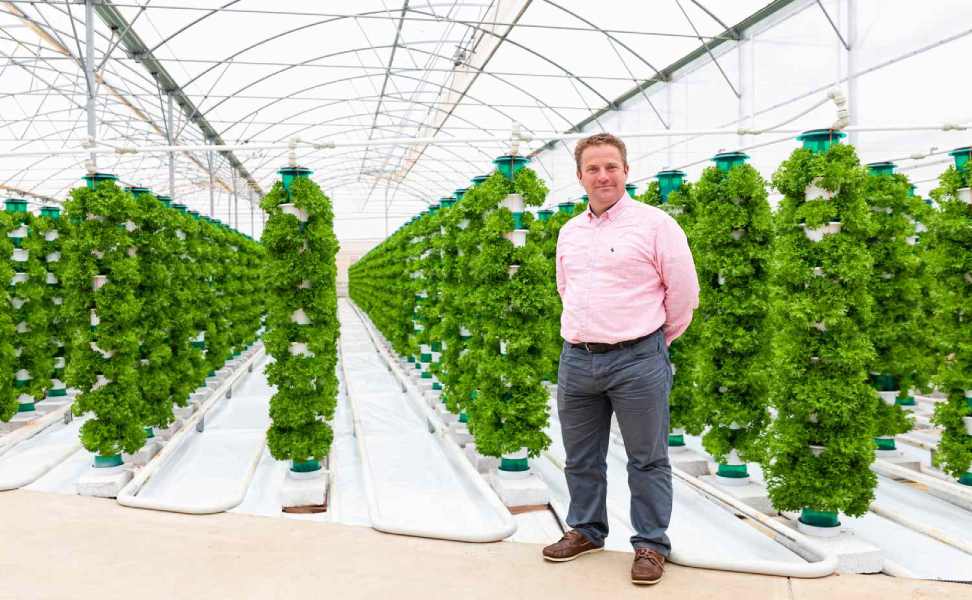
Lotus299, Goldenexch, Msdexch: Vertical farming offers numerous advantages that can revolutionize the way we produce food in urban areas. By utilizing vertical space, this innovative farming method maximizes land efficiency and reduces the need for expansive, traditional farmland. This makes it possible to grow a larger quantity of crops in a smaller footprint, ultimately increasing overall food production sustainably.
Additionally, vertical farming reduces the reliance on long-distance transportation of produce, decreasing the carbon footprint associated with food distribution. This method also allows for year-round crop production, unaffected by external factors such as seasonal changes or weather conditions, providing a consistent and reliable food supply. Not only does vertical farming promote sustainability and self-sufficiency, but it also offers the potential to address food security issues in densely populated areas.
Challenges Faced by Vertical Farming
Vertical farming, though promising, faces several challenges that impede its widespread adoption. One major obstacle is the high initial investment required to set up vertical farming facilities. The technology and infrastructure necessary for vertical farming can be costly, making it inaccessible to many farmers, especially small-scale ones.
Another significant challenge is the energy consumption associated with vertical farming operations. The need for artificial lighting, heating, and cooling systems to simulate ideal growing conditions indoors can result in a high energy demand. This not only adds to the operational costs but also raises concerns about the environmental impact of vertical farming practices.
Types of Crops Grown in Vertical Farms
Aldoexch, Aaonline777, Aaonline247: Vertical farming allows for a diverse range of crops to be grown in a controlled environment, independent of outdoor conditions. Leafy greens such as lettuce, kale, and spinach are popular choices due to their fast growth cycles and high demand in urban areas. Additionally, herbs like basil, mint, and cilantro thrive in vertical farms, providing fresh and flavorful options for consumers.
Beyond leafy greens and herbs, vertical farms also cultivate a variety of vine crops such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers. These crops require vertical support systems to allow for upward growth and optimal fruit production. Root vegetables like radishes, carrots, and beets are also grown in some vertical farm setups, utilizing innovative growing techniques to ensure successful harvests. By diversifying the types of crops grown, vertical farms can offer a wide selection of fresh produce to meet the needs of local communities.
• Leafy greens such as lettuce, kale, and spinach
• Herbs like basil, mint, and cilantro
• Vine crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers
• Root vegetables including radishes, carrots, and beets
Vertical farming technology allows for the efficient cultivation of these various types of crops in a limited space. With careful planning and management of resources such as light, water, and nutrients, vertical farms can optimize growth conditions for each crop type. This level of control enables year-round production regardless of external factors like weather or seasonality.
In addition to traditional fruits and vegetables, some vertical farms specialize in growing specialty crops like microgreens or edible flowers. These unique offerings cater to niche markets seeking gourmet ingredients for culinary purposes. The flexibility of vertical farming systems allows for experimentation with different crop varieties to meet consumer preferences and market demands.
Overall, the versatility of crops that can be grown in vertical farms demonstrates the potential for sustainable agriculture practices in urban environments. By maximizing space efficiency and resource utilization through innovative growing techniques, vertical farming contributes to food security initiatives by providing fresh produce locally sourced from within city limits. As this agricultural method continues to evolve and expand globally, the range of crops cultivated in vertical farms is expected to diversify even further.
What are the benefits of vertical farming?
Vertical farming allows for year-round crop production, reduces water usage, minimizes the need for pesticides, and utilizes urban space efficiently.
What are some challenges faced by vertical farming?
Challenges include high initial investment costs, energy consumption for artificial lighting, potential issues with plant nutrient delivery systems, and the need for specialized knowledge and skills.
What types of crops are typically grown in vertical farms?
Leafy greens such as lettuce, kale, and spinach are commonly grown in vertical farms. Other crops like herbs, strawberries, tomatoes, and microgreens can also be successfully cultivated in vertical farming systems.
Also Read:-
Feature image source:- https://tinyurl.com/yv9nnfha