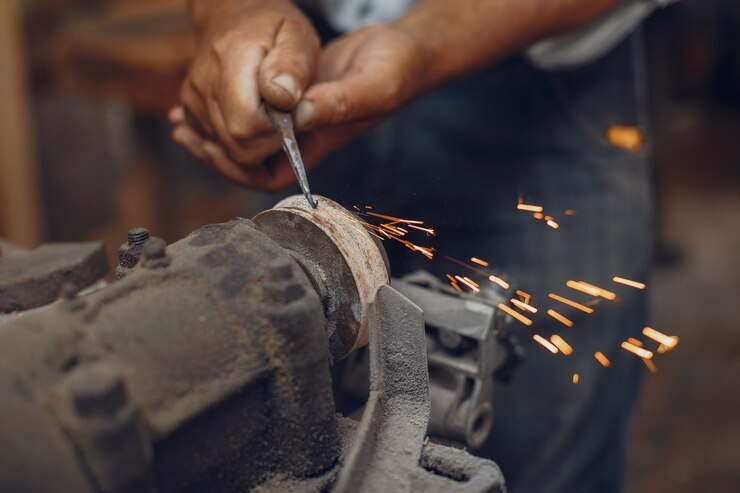
Die-casting, a high-pressure metal casting process, offers numerous advantages in producing complex parts with precision and efficiency.
However, maintaining consistent quality throughout the process is crucial for ensuring product reliability and customer satisfaction. This article outlines essential tips for effective quality control in die-casting.
Understanding the Die-Casting Process
Before delving into quality control measures, it’s essential to grasp the die-casting process. This involves melting metal, injecting it into a mold cavity under high pressure, and rapidly cooling the metal to solidify into the desired shape. Understanding the overmolding and diecasting process helps identify potential quality issues and their root causes.
Key Quality Control Areas
Effective quality control in die-casting involves meticulous attention to several critical areas.
Material Selection and Control:
Material Purity: Ensure that the metal alloy used meets the specified composition and purity standards. Impurities can significantly affect the mechanical properties of the casting.
Temperature Control: Maintain precise temperature control during the melting process to prevent oxidation and ensure consistent material properties.
Material Handling: The die casting manufacturers in China Implement proper handling procedures to avoid contamination and segregation of alloy elements.
Mold Design and Maintenance:
Design Optimization: Collaborate with design engineers to create mold designs that facilitate efficient filling, cooling, and ejection of castings.
Mold Material Selection: Choose suitable mold materials based on the casting alloy and production volume to ensure durability and dimensional stability.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Conduct routine inspections to identify wear, erosion, or cracks in the mold. Implement preventive maintenance to prolong mold life and maintain casting quality.
Die-Casting Machine and Process Parameters:
Machine Calibration: Regularly calibrate die-casting machines to ensure accurate pressure, velocity, and injection time settings.
Process Optimization: Conduct trials to determine optimal process parameters, such as injection speed, holding time, and cooling rate, for each part design.
Monitoring and Control: Implement real-time monitoring of critical process parameters to identify deviations and take corrective actions promptly.
Cooling System:
Efficient Cooling: Ensure adequate cooling of the die to prevent overheating and casting defects.
Cooling Water Quality: Maintain clean cooling water to avoid scale formation and reduce heat transfer efficiency.
Cooling System Maintenance: Regularly inspect and clean the cooling system to prevent blockages and ensure optimal performance.
Inspection and Testing:
In-Process Inspection: Conduct regular inspections of castings during the production process to identify defects early on.
Dimensional Inspection: Use precise measuring equipment to verify that castings conform to specified dimensions and tolerances.
Visual Inspection: Inspect castings for surface defects, such as porosity, cracks, or inclusions.
Mechanical Testing: Perform tests like tensile strength, hardness, and impact resistance to assess the mechanical properties of the castings.
Metallurgical Analysis: Conduct metallurgical analysis to verify material composition and microstructure.
Data Analysis and Process Improvement:
Data Collection: Gather data on process parameters, inspection results, and defect rates.
Statistical Process Control (SPC): Implement SPC to monitor process variability and identify trends.
Root Cause Analysis: Investigate the root causes of quality issues and implement corrective actions.
Continuous Improvement: Utilize data-driven insights to optimize the die-casting process and enhance product quality.
Additional Tips for Quality Control
Operator Training: Provide comprehensive training to operators on quality control procedures, equipment operation, and defect prevention.
Supplier Management: Establish strong relationships with suppliers of raw materials and components to ensure consistent quality.
Cleanliness: Maintain a clean production environment to prevent contamination of castings.
Documentation: Maintain detailed records of process parameters, inspection results, and corrective actions.
Customer Feedback: Incorporate customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and enhance product quality.
By implementing these quality control measures and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, die-casting manufacturers can produce high-quality components that meet customer expectations and enhance their reputation in the market.
In Conclusion:
Achieving consistent quality in die-casting is paramount for manufacturing reliable and durable components. By implementing a comprehensive quality control program that encompasses material management, mold maintenance, process optimization, inspection, and data analysis, manufacturers can significantly enhance product quality and reduce defects.
A strong emphasis on operator training, supplier collaboration, and a clean production environment further contributes to overall quality improvement. By adopting a proactive approach to quality control and continuously seeking opportunities for improvement, die-casting businesses can build a solid reputation for delivering exceptional products that meet customer expectations.
Have A Look :-