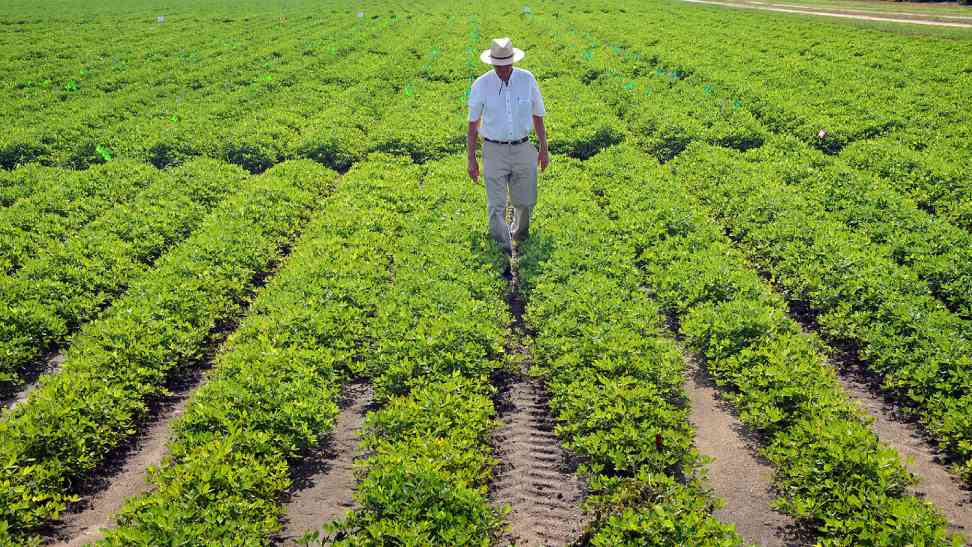
Max66, Arsgroup777, ARS Group Exchange: Genetic engineering in agriculture involves the manipulation of an organism’s genetic material to introduce desirable traits or eliminate undesirable characteristics. This technology allows scientists to enhance crop productivity, improve resistance to pests and diseases, and develop drought-tolerant varieties.
By introducing specific genes into plants, genetic engineering has the potential to create crops with higher nutritional content, longer shelf life, and increased tolerance to environmental stress. These advancements in agricultural biotechnology have revolutionized the way we grow food and have the potential to address global food security challenges in the face of a growing population and changing climate.
Potential Benefits of Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
Genetic engineering in agriculture offers the potential to enhance crop yields and quality, addressing global food security challenges. By introducing traits that make crops more resistant to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses, genetic engineering can help farmers improve productivity and reduce losses. This technology also enables the development of crops with enhanced nutritional content, providing consumers with more nutritious food options.
Moreover, genetic engineering allows for the production of crops with longer shelf lives, reducing food waste and losses during storage and transportation. By creating plants that require fewer inputs like water and pesticides, genetic engineering can contribute to sustainable agriculture practices and environmental conservation. These benefits highlight the significant role that genetic engineering can play in transforming the agricultural industry and ensuring a more secure and sustainable food supply for future generations.
Challenges Faced by Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
Ars247, Wazeerexch, Peachexch: One major challenge facing genetic engineering in agriculture is the issue of public perception and acceptance. Many people have concerns regarding the safety of genetically modified crops and their potential impact on human health and the environment. This skepticism often leads to resistance from consumers and policymakers, creating hurdles for the widespread adoption of genetically engineered crops.
Another significant challenge is the potential for unintended consequences of genetic modification. Despite rigorous testing and evaluation processes, there is always a risk of unforeseen outcomes when introducing novel traits into crops. This uncertainty can make stakeholders hesitant to fully embrace genetic engineering, as the consequences of genetic modifications may not become apparent until after widespread adoption.
What is genetic engineering in agriculture?
Genetic engineering in agriculture involves manipulating the genetic material of plants or animals to create desired traits, such as increased resistance to pests or improved nutritional content.
What are some potential benefits of genetic engineering in agriculture?
Some potential benefits include increased crop yields, reduced reliance on chemical pesticides, improved nutritional content of crops, and the ability to grow crops in harsh environments.
What are some challenges faced by genetic engineering in agriculture?
Some challenges include public perception and acceptance of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), potential environmental risks, the development of resistance in pests and weeds, and regulatory hurdles.
How can the challenges faced by genetic engineering in agriculture be addressed?
The challenges can be addressed through increased transparency and communication with the public, rigorous testing and evaluation of GMOs for safety, implementing proper regulations, and promoting sustainable farming practices.
Must Read :